The Ministry is migrating nzmaths content to Tāhurangi.
Relevant and up-to-date teaching resources are being moved to Tāhūrangi (tahurangi.education.govt.nz).
When all identified resources have been successfully moved, this website will close. We expect this to be in June 2024.
e-ako maths, e-ako Pāngarau, and e-ako PLD 360 will continue to be available.
For more information visit https://tahurangi.education.govt.nz/updates-to-nzmaths
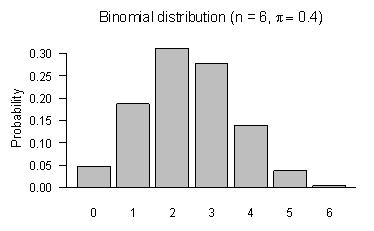
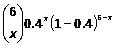 for x = 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6
for x = 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6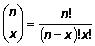 is the number of combinations of n objects taken x at a time.
is the number of combinations of n objects taken x at a time.